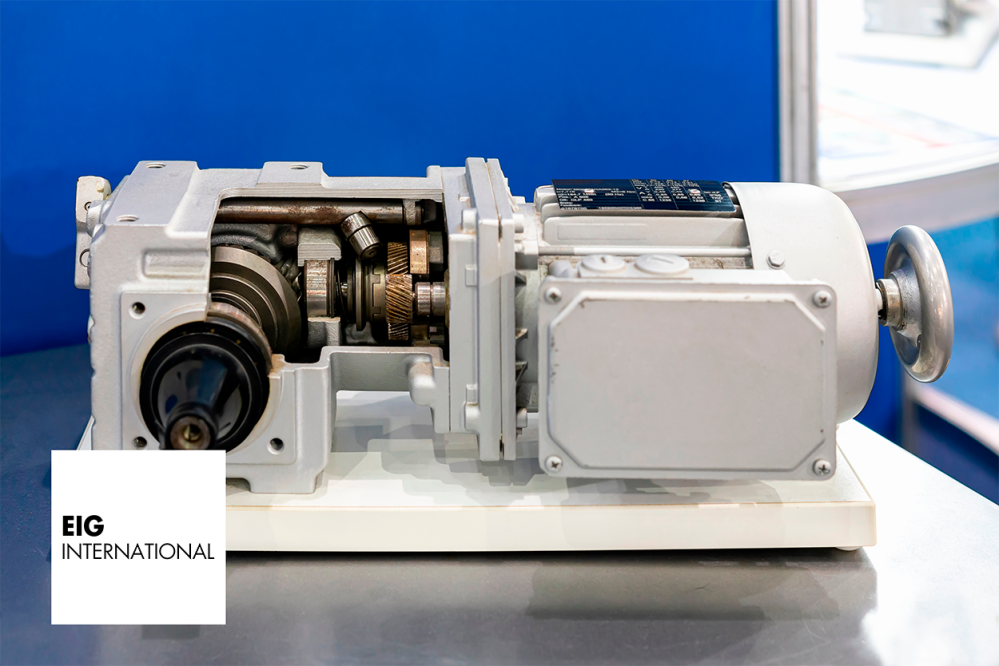
Gearboxes play a vital role in a wide range of industries and applications. Their primary purpose is to enhance output torque or adjust the speed of a motor, measured in RPM. Typically, a gearbox connects to one end of a motor shaft, and the gear ratio determines the resulting torque and speed. Gearboxes come in various designs and specifications to cater to different needs across agricultural, industrial, construction, mining, and automotive sectors. In this article, we will explore different types of gearboxes, highlighting their key characteristics and applications.
EIG International FZ-LLC is your trusted supplier of diverse gearboxes
At EIG International FZ-LLC, we take pride in being a leading supplier of a wide range of gearboxes. With our commitment to quality and reliability, we strive to meet the diverse needs of industries worldwide. Our extensive product lineup and expertise make us a preferred choice for businesses seeking efficient and high-performing gearbox solutions.
Now, let's delve into the various types of gearboxes commonly utilized in industrial and automotive settings, showcasing their unique features and applications.
Helical Gearbox:
The helical gearbox, known for its compact size and energy efficiency, finds widespread use across industries, particularly in heavy-duty applications. Industries such as plastics, cement, and rubber rely on helical gearboxes, which excel in low-power applications like crushers, extruders, coolers, and conveyors. These gearboxes stand out due to their inclined mounting angle, enabling smooth and continuous engagement of a greater number of teeth, resulting in enhanced performance and durability.
Coaxial Helical Inline Gearbox:
Designed for heavy-duty performance, coaxial helical inline gearboxes are renowned for their quality and efficiency. Manufactured to precise standards, these gearboxes provide optimal load handling and transmission ratios. With their robust construction, they are ideal for demanding applications across various industries.
Bevel Helical Gearbox:
The bevel helical gearbox features a series of curved teeth positioned on a cone-shaped surface near the unit's rim. Its primary purpose is to facilitate rotational motion between non-parallel shafts. Industries such as quarries, mining, and conveyors commonly employ this gearbox to meet their specific needs.
Skew Bevel Helical Gearbox:
Built with a sturdy and monolithic construction, the skew bevel helical gearbox excels in handling heavy loads and challenging applications. Once properly installed on the motor shaft output, these gearboxes deliver exceptional mechanical advantages. With a wide range of teeth and gear configurations available, finding a gearbox that precisely matches your requirements is easily achievable.
Worm Reduction Gearboxes:
When it comes to propelling heavy-duty tasks, worm reduction gearboxes are the go-to choice. They excel in applications requiring significant speed reduction between intersecting shafts. These gearboxes feature a large-diameter worm wheel and a worm or screw that engages with the gearbox's outer teeth. As the worm rotates, it imparts a screw-like movement, resulting in smooth motion of the wheel. Industries such as fertilizers, chemicals, and minerals rely on worm reduction gearboxes for their robustness and reliability.
Planetary Gearbox:
Utilizing a central sun gear surrounded by three or four planet gears, a planetary gearbox efficiently distributes power evenly among the gears, generating high torque within a compact design. This type of gearbox finds applications in cutting-edge technologies such as robotics and 3D printing. Its exceptional durability, precision, and specialized functionality make it an ideal choice for precise applications. Available in solid or hollow configurations with various mounting options like flange, shaft, or foot, planetary gearboxes offer versatility to suit different equipment requirements.
Automotive Gearboxes: Powering Efficient and Seamless Transmissions
Manual Transmission:
Manual transmissions, commonly known as "stick shifts" or "conventional" transmissions, provide drivers with full control over gear selection using a movable gear selector and a clutch. This traditional transmission type allows for a personalized driving experience and is widely used in different automotive vehicles.
Sliding-Gear Transmission:
Sliding-gear gearboxes were prevalent in earlier automobiles. These transmissions involve the main drive gear and cluster gear continuously in motion when the transmission is in neutral. By pressing the clutch pedal and shifting the shifter handle, the position of the shift linkage and forks change, causing a gear above the cluster gear to move along the main shaft, thereby transferring power to the drive wheels.
Constant-Mesh Transmission:
Constant-mesh transmissions, also referred to as synchronized transmissions, maintain the gears in constant motion. This is made possible by allowing the gears to freely rotate around the main shaft. To lock the gears into position, dog clutches are employed when required. Synchronizers prevent clashing or grinding during shifting, ensuring a smooth and seamless driving experience.
Pre-selector Transmission:
The pre-selector transmission represents an earlier form of manual transmission that emerged before the advent of fully automated transmissions. It underwent various modifications and improvements as automakers explored new design concepts.
Automatic Transmission:
Automatic transmissions, in contrast to manual transmissions, operate differently and offer convenience to drivers. They feature gear positions such as Park, Reverse, Neutral, and Drive, often accompanied by additional modes like Sport or manual shift mode. Lever controls in automatic transmissions serve as electrical switches that relay commands to the gearbox's controlling software, leading to seamless gear shifts. Some manufacturers have even replaced traditional levers with buttons, paddles, or dials to enhance the transmission control experience.
Torque Converter:
The most prevalent type of automatic transmission utilizes a torque converter to transfer rotational force from the engine to the wheels. The torque converter acts as a fluid coupling, allowing smooth acceleration and deceleration without stalling the engine. However, due to the curved shape of the turbine blades within the converter, there is some loss of efficiency. Torque converters are known for their ability to deliver smooth acceleration at low speeds and responsiveness at low engine RPMs.
Automated-Manual Transmission:
Automated-manual transmissions combine the convenience of automatic transmissions with a conventional clutch and gear layout found in manual transmissions. By utilizing sensors, actuators, processors, and pneumatics, these transmissions simulate manual gear usage. While they offer excellent fuel economy over long distances, they may exhibit jerky engine performance at low speeds and during acceleration.
Dual-Clutch Transmissions (DCT):
Dual-clutch transmissions are rapidly gaining popularity as the most widely used type of automatic transmission for both gasoline and diesel vehicles. Referred to as DSG (direct shift gearbox) by most Volkswagen Group brands, these transmissions offer a direct and engaging driving experience while being highly efficient and user-friendly. In many cases, they provide better fuel efficiency and performance than manual transmissions. Some slight jerkiness may be experienced at low speeds or during shifts between the first and reverse gears, but overall, they offer an excellent balance of performance and efficiency.
Continuously Variable Transmission (CVT):
Unlike traditional gear-based transmissions, a CVT employs a cone-shaped mechanism with a band and a second axle instead of fixed gears. By adjusting the position of the band along the cone, the gear ratio can be infinitely varied within the upper and lower limits. This allows for optimal adjustment of the gear ratio based on the desired balance between fuel economy and performance. Hybrid vehicles, in particular, benefit from CVTs as they help optimize the workload distribution between the gasoline engine and electric motor.
Choose EIG International FZ-LLC for Reliable Gearbox Solutions
As a trusted supplier of various gearboxes, including those mentioned above, EIG International FZ-LLC stands ready to fulfill your industrial and automotive gearbox needs. Our dedication to delivering high-quality products ensures that you receive efficient and reliable solutions for your equipment and machinery. Partner with us to experience the difference that our expertise and extensive product range can make in enhancing the performance of your operations.